It probably won’t surprise most vegetable gardeners that insects outnumber humans many millions of times over. While some insects can be beneficial for certain plants, gardeners are all too familiar with the destruction of many tiny crawly critters.
Luckily, nature uses a lot of non-toxic methods to dissuade and manage damaging pests. The following 6 actions can assist a gardener minimize bug issues without poisonous chemicals. Keep in mind: Avoidance is constantly the very first and finest line of attack.
1. Build Healthy Soil
Soil supplies the nutrients, root, water, and oxygen support that plants require to thrive. Research reveals that the healthier the soil, the much better plants are able to withstand pest attacks. http://research.wsu.edu/resources/files/no-till.pdf Building healthy, fertile, living soil is the most crucial way to avoid pest problems.
Build healthy soil with these five practices:
– Limitation Soil Disruption
A growing body of research study recommends that regularly turning the soil has different disadvantages. http://research.wsu.edu/resources/files/no-till.pdf It leaves the soil surface bare, encourages runoff, triggers soil compaction and disintegration, and harms soil microorganisms and earthworms. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167198700001732 Keeping disturbance to a minimum maintains the living systems in soil. Rather, layer amendments on top, and let the earthworms aerate the soil.
– Compost.
Start a. garden compost bin and include one to 2 inches of well-decomposed compost to the garden each spring to supplement nutrition in the soil and motivate a preferable soil structure.
– Mulch.
Include 2 to 4 inches of turf clippings or trimmed leaves to the garden when plants are about 4 inches high to decrease water evaporation, reduce weeds, moderate soil temperature, avoid soil compaction, and add slowly-decomposing natural matter to the soil.
– Turn crops.
When plants are consistently planted in the very same beds, crop yields reduce. That’s partly since soil-dwelling pest populations, such as grubs, wireworms, and maggots, boost. Strategy to. turn plant families. to brand-new beds each season to keep bugs on the run.
– Plant cover crops.
At the end of the growing season, plant a. cover crop such as ryegrass, peas, or clover, to boost the soil’s fertility, lessen disintegration over cold weather, reduce weeds, and enhance the soil structure. In spring, cover the crop with mulch or enable chickens to graze.
2. Bring In Beneficial Predators.
Keep in mind, not all bugs are bad. Numerous really assist plants grow by pollinating, breaking down waste, and gobbling up bugs. The trick is to understand which bugs benefit your plants and which can end up being an issue.
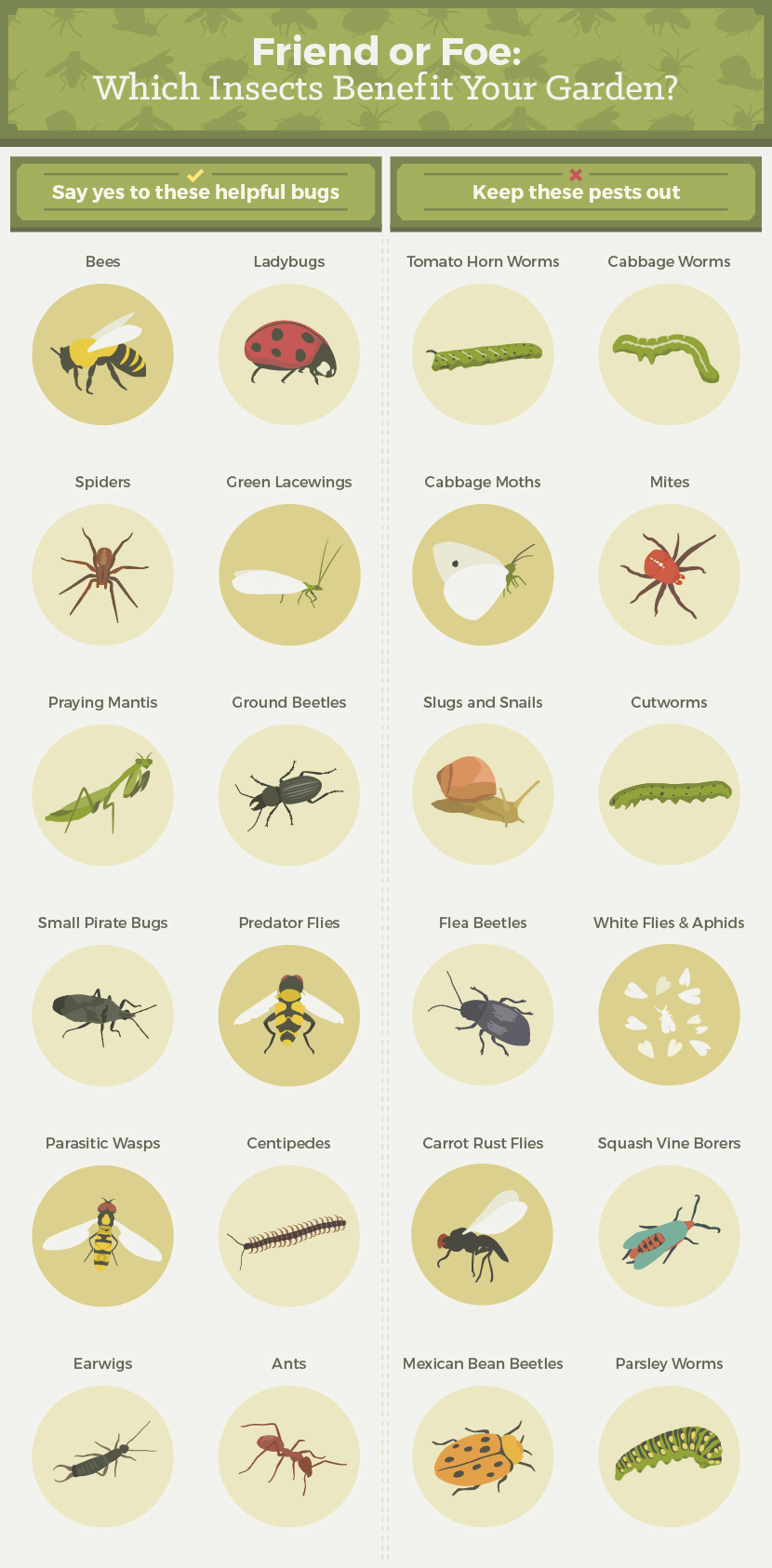 In general, keep the garden as diversified as possible and motivate year-round blooming to draw in varying kinds of useful pests. The following plants are particularly attractive to the predators that assist control pest populations:. http://www.finegardening.com/attracting-beneficial-insects
In general, keep the garden as diversified as possible and motivate year-round blooming to draw in varying kinds of useful pests. The following plants are particularly attractive to the predators that assist control pest populations:. http://www.finegardening.com/attracting-beneficial-insects
• Native flowering plants, especially those with daisy-shape blooms
– Tansy.
– Fennel.
– Mint.
– Carrots.
– Dill.
– Sweet alyssum.
– Marigolds.
– Parsley.
– Coriander.
– Zinnia.
3. Screen the Garden.
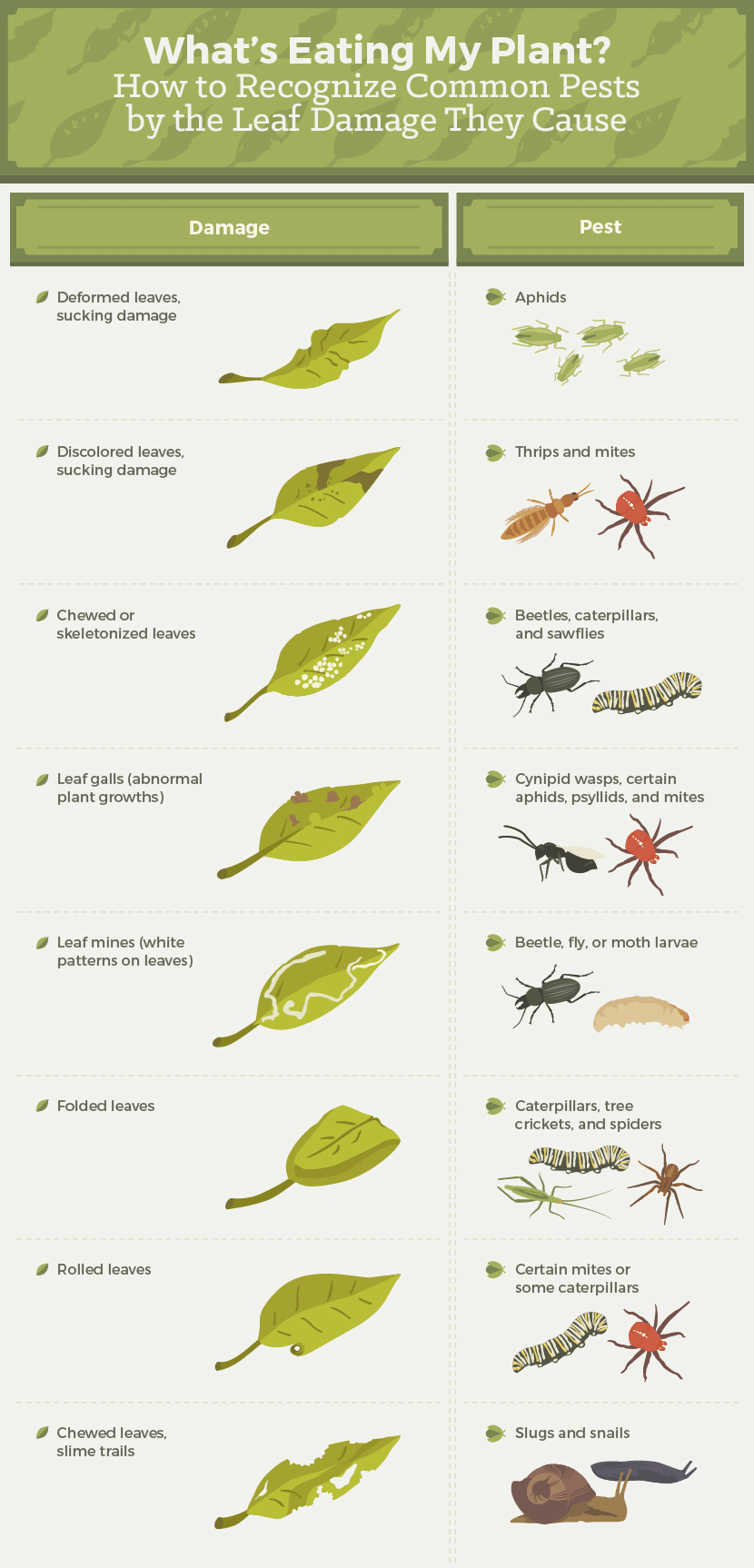
The fact is, every garden enthusiast will share some harvest with pests. Even in a garden with healthy soil that is buzzing with useful bugs, it’s a great idea to closely monitor crops for pest damage. Make certain to inspect the undersides of leaves, where bugs leave and hide egg sacs.
4. Choose Whether to Tolerate or Take Action.
If pest damage is minimal, natural garden enthusiasts may just want to endure insects, since any bug control can likewise damage advantageous pollinators and predators.
It’s generally safe to eat a little harmed fruit and vegetables, so long as you follow these guidelines:. http://www.gardensalive.com/product/eating-insect-damaged-crops/
• Toss anything that’s been munched on by rodents or raccoons.
– Toss anything that an animal has defecated on.
– Toss any leaves that have a squiggly white design. It’s caused by leaf miners, which are still inside the leaves.
– It’s generally safe to consume produce that has a few holes or has been munched on by insects. Cut off harmed locations and enjoy the rest.
If pest damage is expensive to tolerate, begin with the least invasive control approach.
5. Mechanical Pest Solutions.
These hands-on techniques use simple devices, devices, or natural ingredients to provide a protective barrier between insects and plants. Although the components or devices might appear non-toxic and harmless, numerous can injure or hurt bees and other advantageous bugs. It’s constantly essential to be selective.
– Barriers.
Nets, fences, and paper collars keep bugs and other animals away from plants. Floating row covers. — transparent plastic or fabric covers that let sunshine in– keep beetles, flea beetles, and many other bugs at bay. Barriers can avoid pollination, so row nets and covers ought to be raised while flowers are flowering.
– Handpicking.
Plucking insects and egg sacks off plants by hand is a non-toxic and effective way to control them, although it can be labor-intensive.
– Traps.
Mechanical traps entice pests far from plants, permitting them to be removed from the garden. Different traps can be acquired at garden shops or made at home. Develop your own slug and snail trap by nailing strips of wood on a board. Put it in the garden, with the disrobe, so the board is slightly propped off the ground. Slugs and snails will climb under it and can be easily accompanied away from the garden.
– Water Pressure Sprays.
A powerful stream of water removes aphids and spider termites, however the procedure should be duplicated regularly. Only utilize on strong plants, and allow plants to dry in between sprays to prevent illness triggered by over-watering.
– Insect Vacuums.
Handheld, battery-powered vacuums can be utilized to get rid of bugs from plants. Shake the plant and vacuum the insects that fall or fly off.
– Food Grade Diatomaceous Earth.
Diatomaceous earth a powder made from fossilized aquatic organisms, permeates the exoskeleton of bugs, dehydrating and eliminating them. Spray it around the stems of plants to keep crawling pests away. It is safe for people and family pets, although it should not be taken in. It just works when dry, so reapply after rain and watering. Diatomaceous earth eliminates both pests and useful pests.
– Insecticidal Soap.
Spraying diluted soap on plants can discourage a number of bugs. Utilize a natural soap with no cleaning agent or ingredients, such as. castile soap . Try 5 tablespoons of soap per gallon of water and test on a small portion of the plant. Dilute even more if the spray causes leaf damage. Soap eliminates both bugs and helpful insects.
– Horticultural Oils.
Horticultural oils. are petroleum- or plant-based oils blended with emulsifiers so they can be contributed to water and sprayed on plants. They smother and toxin scale, aphids, mites, and other soft-bodied insects. Horticultural oils eliminate both pests and advantageous pests.

6. Chemical Cures.
If all else stops working, it might be time to try a natural pesticide. Use only chemicals. approved by the USDA. for usage by natural growers, and utilize them selectively. Start with the least poisonous and most particular solution initially, and use it at night when bees are least active.
The Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation uses these guidelines on the natural mechanical and chemical pesticides that are most safe for bees:. http://www.xerces.org/wp-content/uploads/2009/12/xerces-organic-approved-pesticides-factsheet.pdf
- Bacillus thuringiensis.
- Garlic.
- Kaolin clay.
- Corn gluten.
- Gibberellic acid.
Moderately Toxic.
- Boric acid.
- Neem.
- Ryania.
- Adjuvants.
- Horticultural vinegar.
- Copper.
- Lime sulfur and sulfur.
Highly Poisonous.
- Diatomaceous earth.
- Insecticidal soap and oil.
- Pyrethrins.
- Rotenone.
- Sabadilla.
- Spinosad.
- Copper sulfate.
Non-Toxic.
Cooking Area Remedies for Garden Pests.
Some efficient bug solutions can be found in the kitchen. Constantly test homemade solutions on a small part of the plant to ensure they will not harm it, and never ever apply on a brilliant or hot bright day, which could cause plants to burn.
 By building healthy soil, inviting helpful insects, developing a pest tolerance level, and selectively managing pests that can’t be endured, gardeners create a lovely and productive ecosystem that is safe for all animals.
By building healthy soil, inviting helpful insects, developing a pest tolerance level, and selectively managing pests that can’t be endured, gardeners create a lovely and productive ecosystem that is safe for all animals.
Article source: http://www.fix.com/blog/common-garden-pests-and-how-to-get-rid-of-them/?crlt.pid=camp.ScHcPjqWj38b
SHARE IT SO OTHERS CAN FIND THE BEST GARDENING INFO




